In this tutorial you will learn how to install the Debian based Kali Linux operating system. Kali is designed for digital forensics as well as penetration testing. Kali is very useful to have installed if you are currently in or entering into the cyber security field. One of the main benefits of Kali Linux are its approximately 600 penetration testing tools preinstalled.
Download Latest Kali Version
The first step is to download the latest version of Kali Linux from the official website.
Boot USB or Select ISO
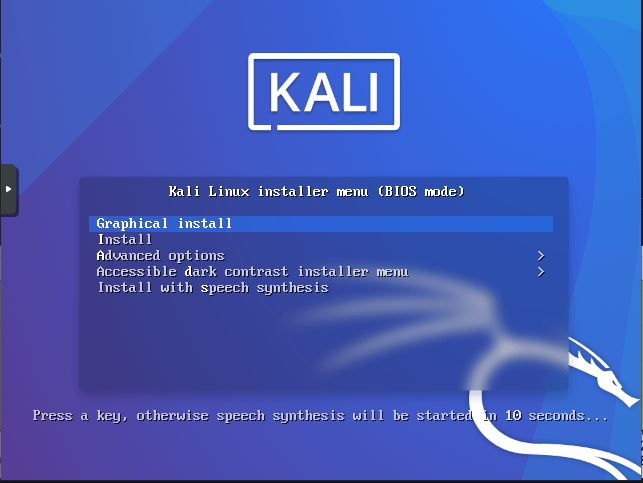
Next you will need to make a bootable USB drive using the Kali ISO file. You can read this tutorial on creating a bootable Linux USB drive using Rufus to learn more. After you create the bootable Kali USB drive, insert it into your computer and select the USB at boot. If you are using a virtual machine, simply select the Kali ISO as your boot device. Once you are booted into the installer, select “Graphical Install”.
Select System Language
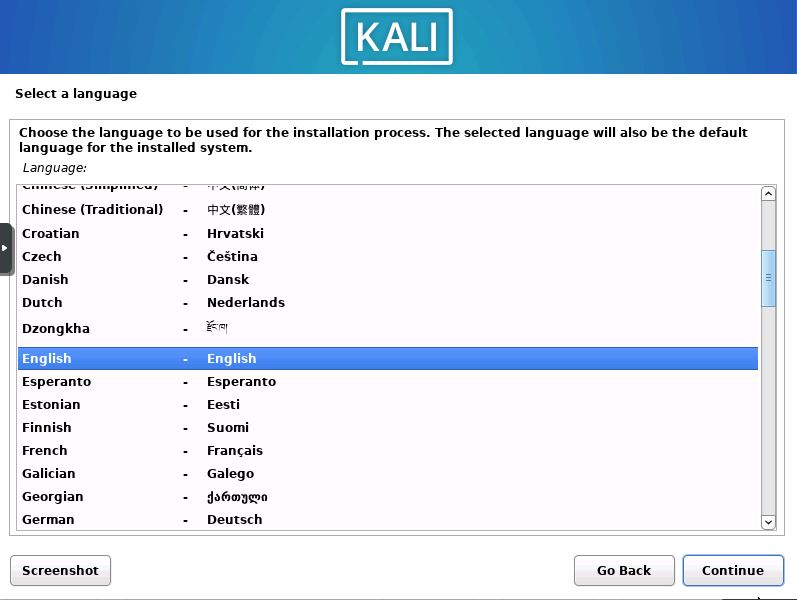
Now you will select the language you would like to use.
Select Location
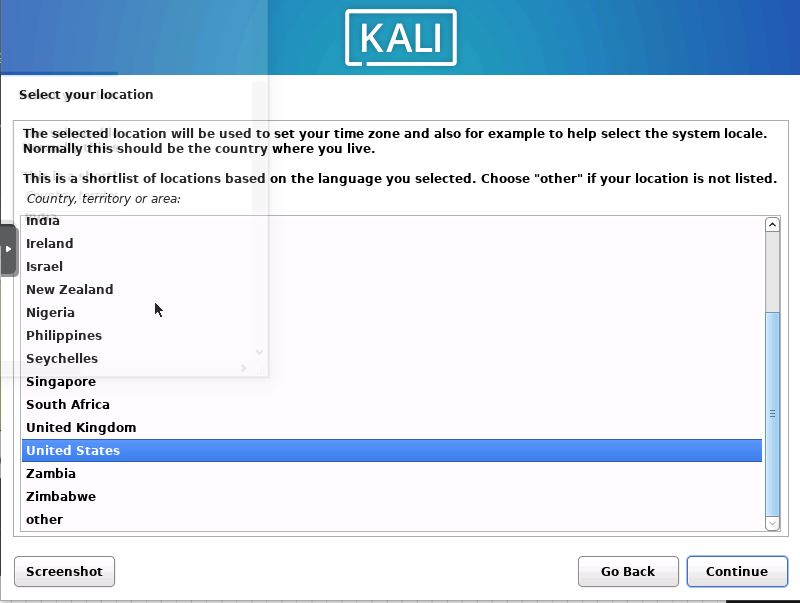
Next select your location.
Select Keyboard Layout
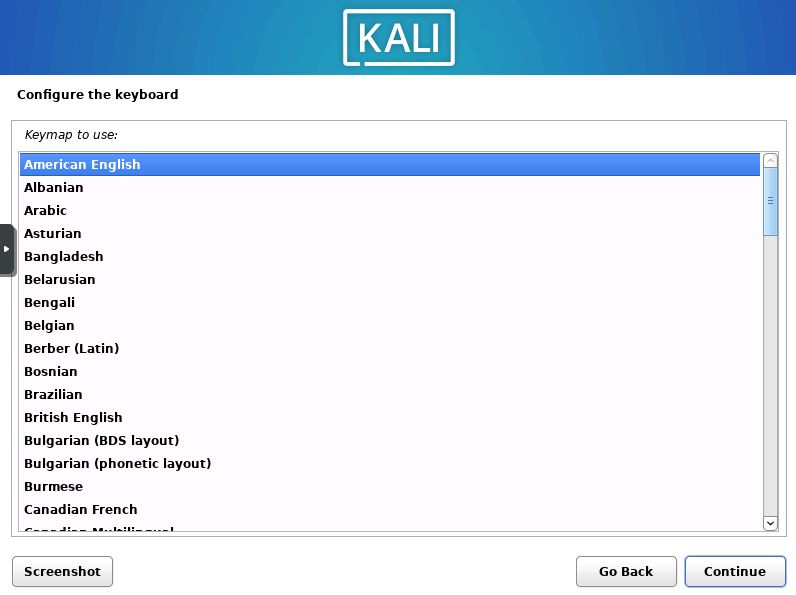
Afterwards you will need to select a keyboard layout.
Choose Hostname
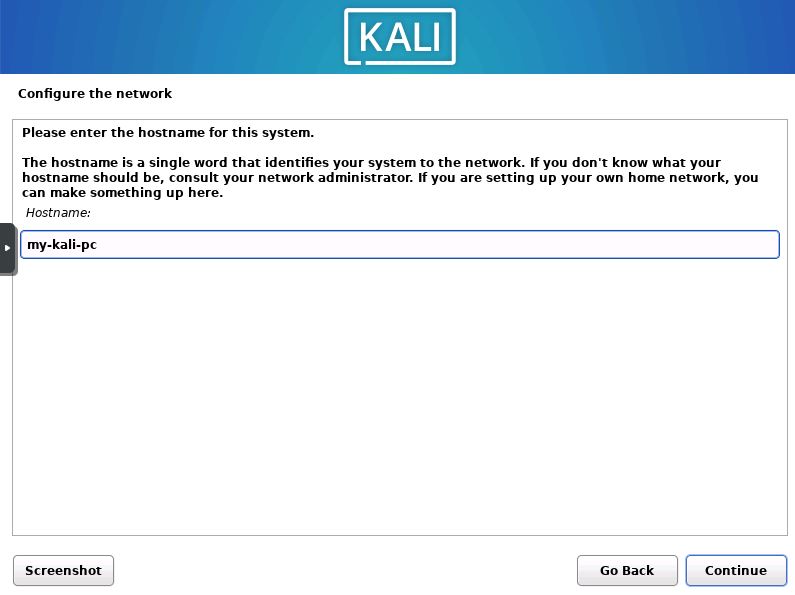
Now you will choose a hostname for the installation. You can enter any name you would like into the box.
Enter Domain Name (optional)
The next step is to select a domain name. This step is optional, and usually unused. So I will be skipping it.
Set Account Name
Now you will enter the full name for the new user, afterwards press the “Continue” button.
Enter a Username
Next you will need to set the username for the account. Enter it into the box and then press “Continue”.
Choose a Password
After setting the username you will need to create a password for the new user. Enter the password and confirmation password.
Select the Timezone
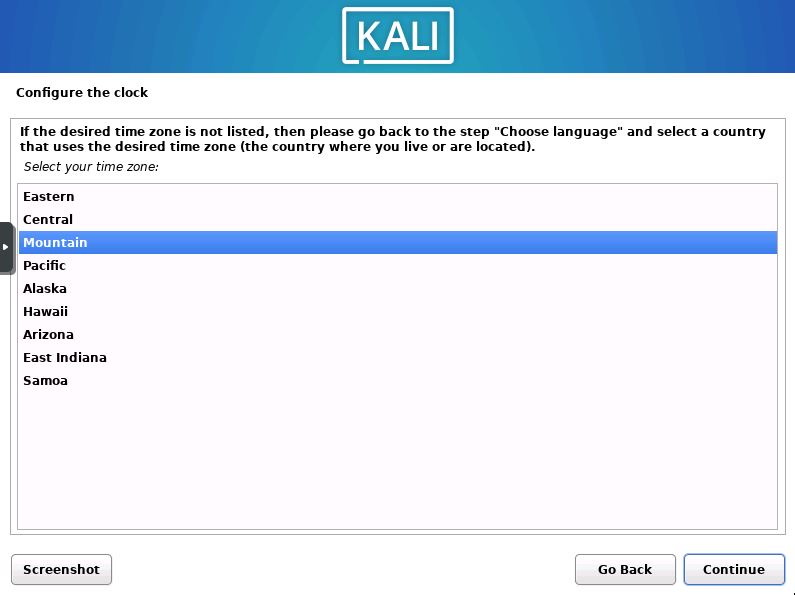
Now you will set the system timezone. This will set the clocks to the correct time.
Set Partitioning Method
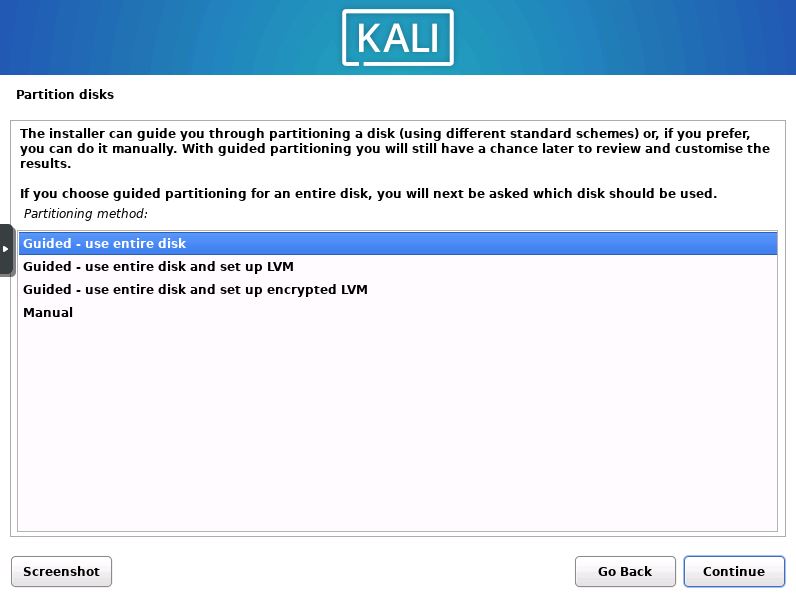
Next you will choose from four different partitioning schemes. Select “Guided – use entire disk” unless you want to encrypt the disk, then press “Continue”.
Select the Disk for Installation
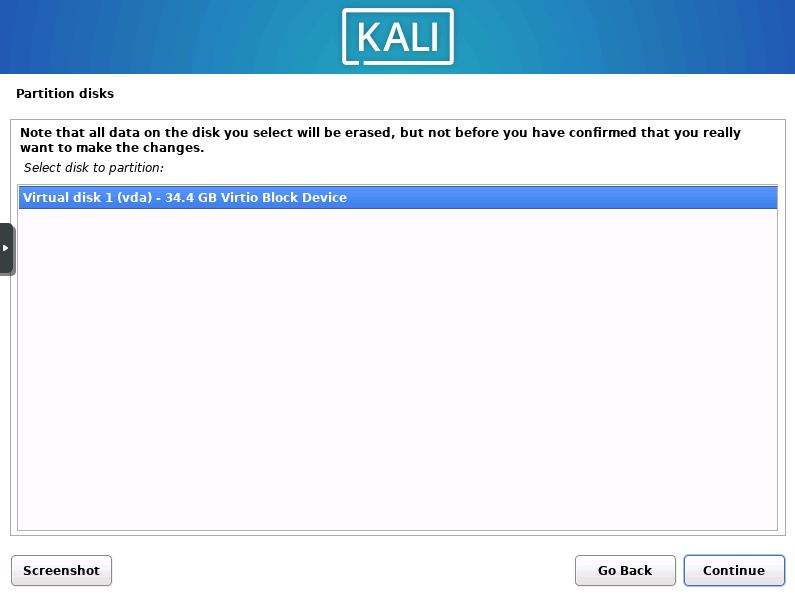
Now the installer will ask you which disk you would like to install Kali onto. (note, all data will be deleted from the selected device)
Choose Partition Scheme
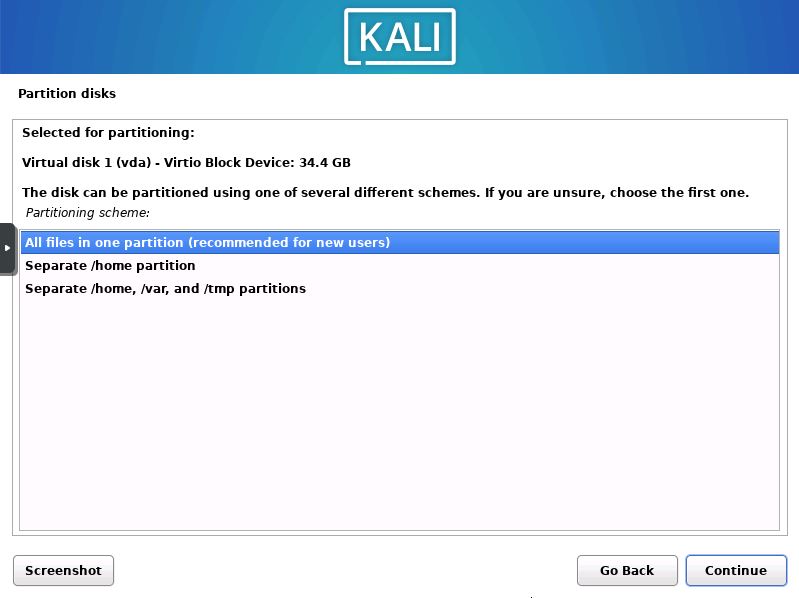
The installer will then ask if you would like a separate home partition, or all files in the same partition. I recommend new users choose the all files in one partition option.
Confirm Partition Changes
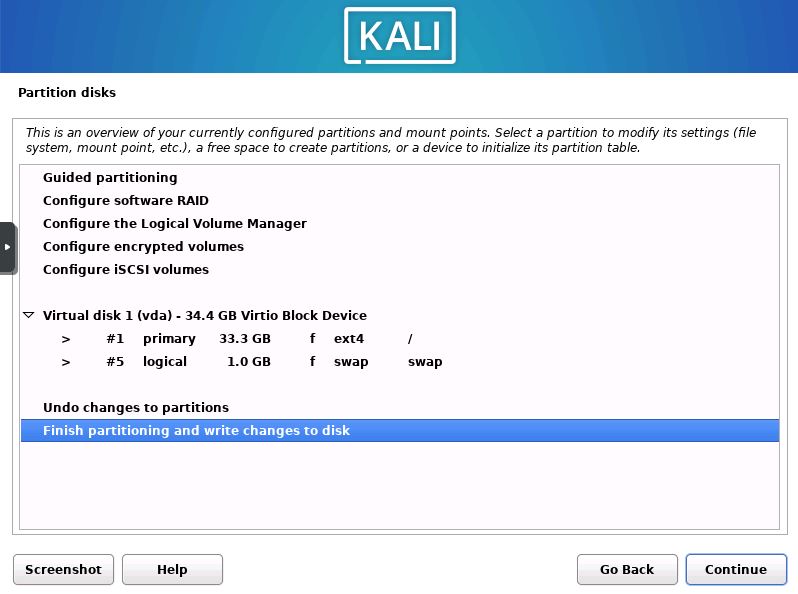
Now you will be shown a overview of the changes that are due to take place. Look them over then press “Finish partitioning and write changes”.
Confirm Write Changes
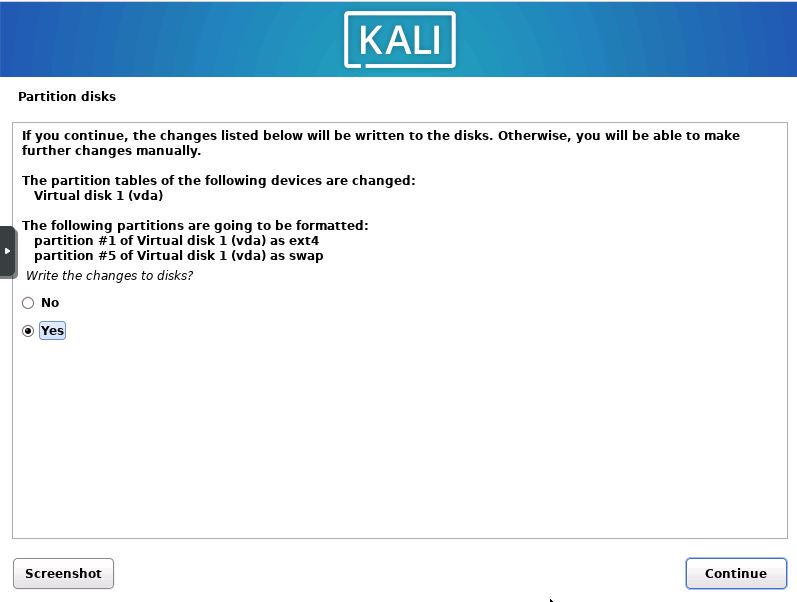
You will then be prompted with a confirmation asking if you want to write the changes to the disk. Click “Continue”.
Wait for the Base System to Install
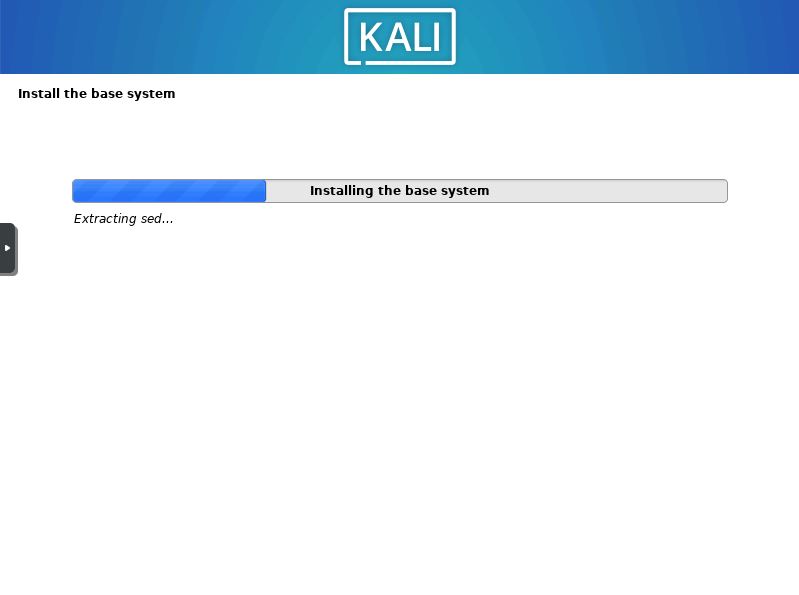
Wait for the base system to finish installing. This can take a while depending on the performance of your computer.
Software Selection

Now you will be asked which desktop environment you want. As well as what software you would like installed. I recommend keeping all options to default as displayed in the above screenshot.
Install Grub
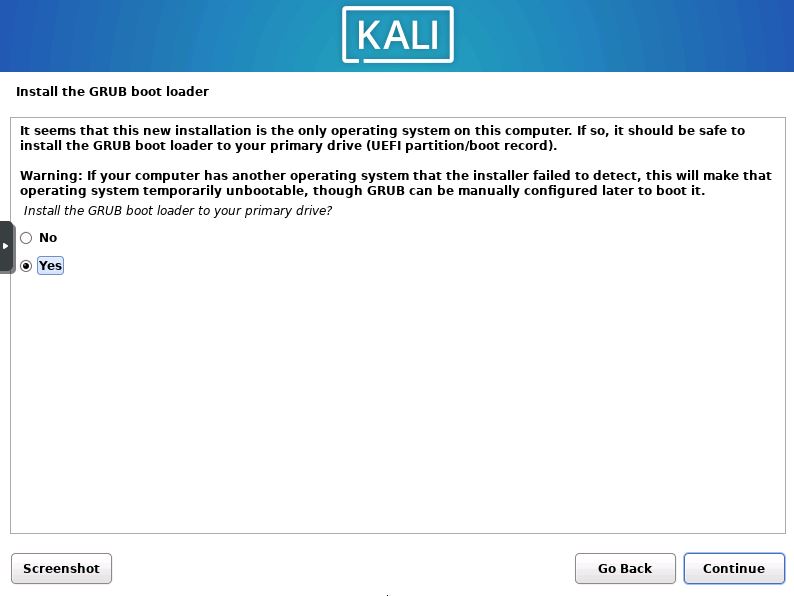
You will then receive a prompt asking you if you would like to install the Grub boot loader. Select the Yes checkbox and press “Continue”.
Select Grub Device
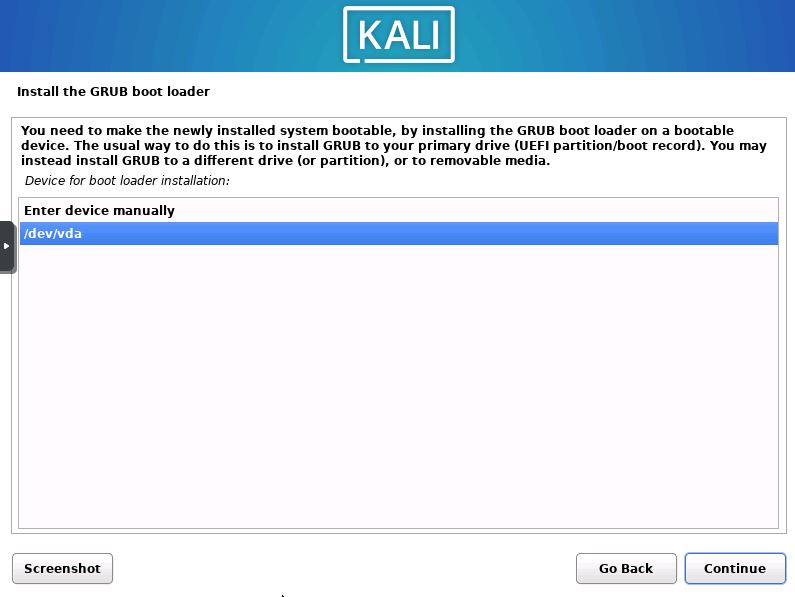
Now you will need to select which device to install Grub onto. Select the /dev/x device and then “Continue”.
Reboot the System
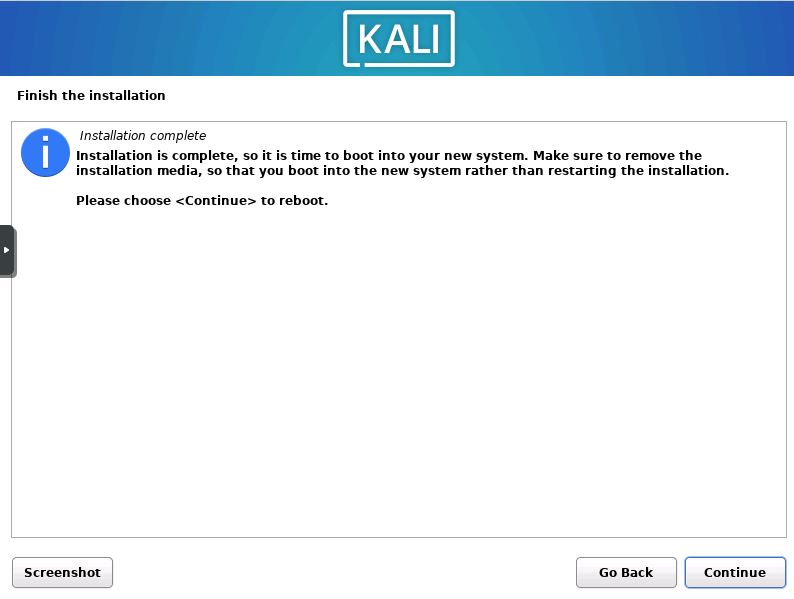
Once you see this screen you are almost ready to begin using Kali. Simply remove your installation media and reboot the system.
Installation Complete

Once the system has rebooted you will see the login screen. You have now completed the installation of Kali 2022.3. Enter the credentials that you created earlier to start using Kali.
Additional Questions?
If you have any additional questions or thoughts feel free to comment them below.
Related Resources
View our 5 Reasons to Switch from Windows 10 to Linux.
Learn How to Create a Mapped Network Drive in Windows 10.
Click here to learn How to Easily Create a Bootable Linux USB Drive using Rufus.
View our OS Installs Category.
Learn more cool things in Windows with our Windows Tutorials.
View all of our available online tools and converters at Formatswap.com.